09 January 2025 | Ronald Albert, Maciel Zortea | IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters
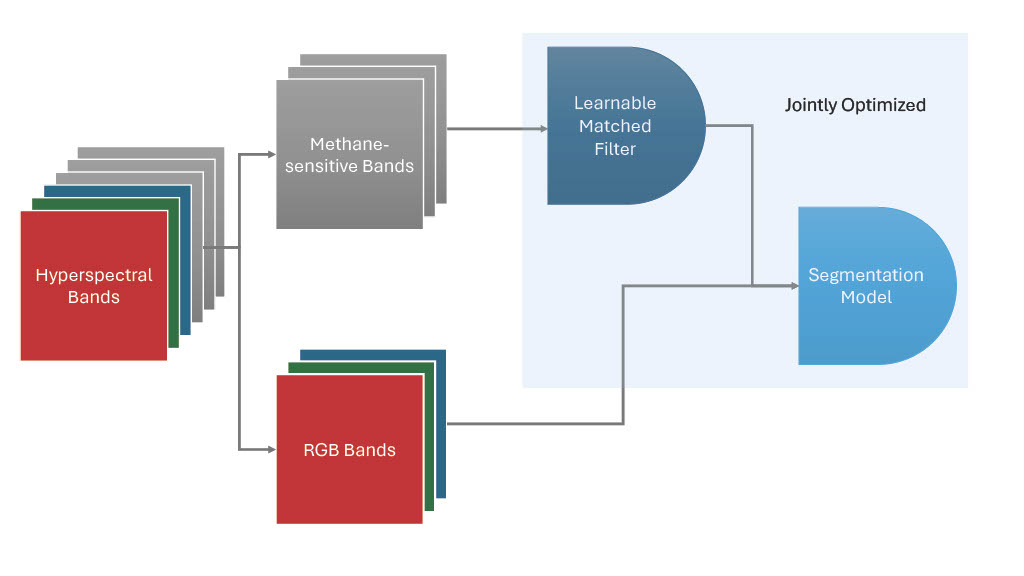
Methane emissions are a major contributor to global warming, making the detection and monitoring of anthropogenic methane sources, such as oil and gas operations and landfills, a critical task. Remote sensing using hyperspectral sensors has proven to be a valuable tool for this purpose. However, traditional methane detection algorithms based on matched filters often produce spurious results and require laborious post-processing to accurately identify actual plumes. In this paper, we propose a novel approach for estimating the target signature of a matched filter as a learnable layer integrated into a user-selected segmentation model, trainable in an end-to-end manner. By considering the signature as a parameter of the segmentation model, our methodology enables the signature to adapt both to the task and the user-selected segmentation approach. We use hyperspectral images from the EMIT instrument and their associated publicly available methane plumes to train deep learning segmentation models. Our results show consistent improvements in both convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and transformer architectures, as demonstrated by the F1 segmentation score increasing by approximately 18% compared to the baseline values. This allows for more accurate and automated plume segmentation, ultimately aiding in the identification of methane leaks from point source emitters.
DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2025.3527871
